Standard test block is the basis of inspection, based on the earliest "Dutch test block", after decades of development, now the domestic power, petroleum, shipbuilding, steel structure, crane and other industries according to the inspection needs, have their own industry inspection standards, and the corresponding standard test block. Our company has participated in the compilation of national inspection standards since the 1980s, and has participated in the revision of more than 20 inspection standards. In 2013, I participated in the revision of GB/T11345-2013 "Ultrasonic Testing Technology, testing Grade and Evaluation of Weld Nondestructive testing" standard, and designed and made corresponding standard flaw detection test blocks according to the standard provisions. At the same time, I also participated in the preparation and discussion of the ultrasonic part of NB/T 47013 (JB/T 4730) "Non-Destructive Testing of Pressure Equipment", which provided a large number of experimental test blocks for the expert group and collected more data with the experiment, providing an important basis for the revision of the standard. Our company has extensive exchanges with international industry colleagues, many times received Germany, Britain, Russia, India, Japan, South Korea and other friends to visit. Products exported to the United States, Canada, Russia, India, South Korea, Japan, Germany, France and so on.
International standard test block
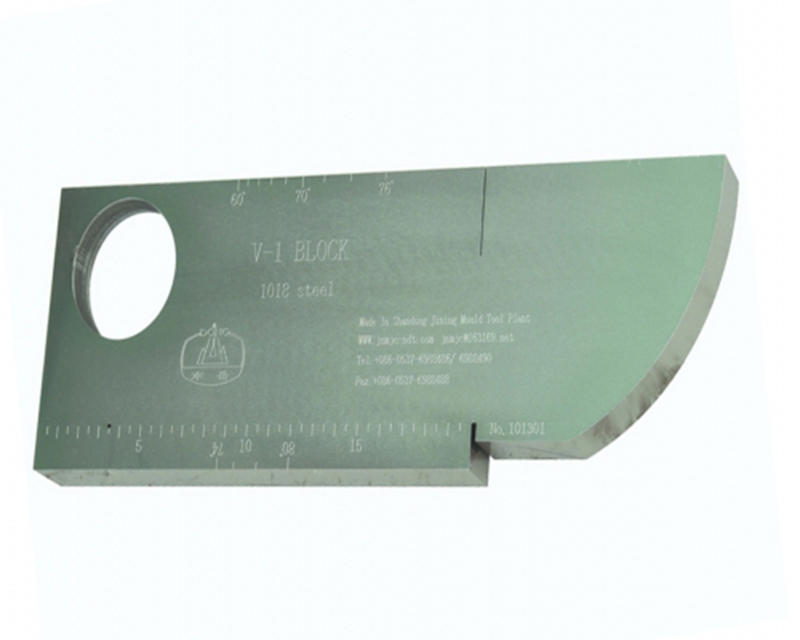
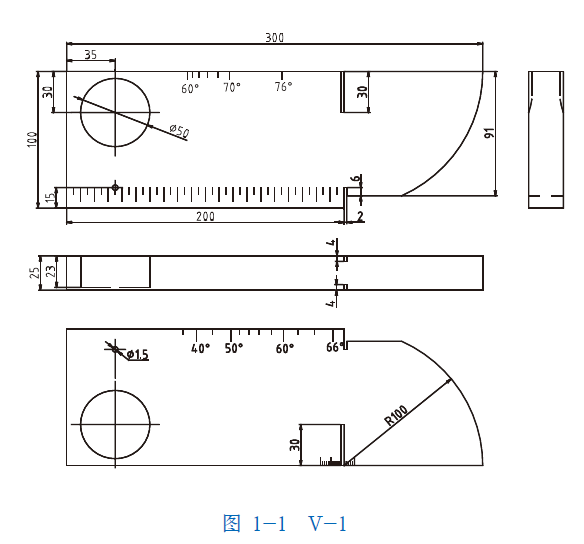
IIW test block (V-1 test block) is also called Dutch test block. It is an international standard test block recommended by the International Institute of Welding (IIW) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Figure 1-1 shows the shapes and dimensions:
Key points of use:
(1) The dynamic range, horizontal linearity and longitudinal wave detection range of the flaw detector can be determined by using the test block thickness of 25mm;
(2) The Angle of refraction of the inclined probe and the sensitivity margin of the longitudinal wave straight probe were measured by φ50 arc and φ1.5 through hole; It can also estimate the size of the blind area of the straight probe and measure the penetration ability of the combination of the instrument and probe.
(3) Use R100mm arc surface to determine the incident point and blind area of the inclined probe, and can correct the time axis ratio and zero;
(4) The longitudinal resolution of the straight probe can be measured by using three notch planes ranging from 85mm, 91mm and 100mm;
(5) Use the right Angle edge of the test block to measure the beam-deflection Angle of the inclined probe.

| 美國標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊ASME-1# | |
| 美國標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊ASME-2# | |
| 美國標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊ASME-3# | |
| 美國標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊ASME-4# | |
| 美國標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊ASME-5# | |
| 美國標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊ASME-6# | |
| 英國標(biāo)準(zhǔn)A3試塊 | |
| DC型距離校準(zhǔn)試塊 | |
| SC型靈敏度校準(zhǔn)試塊 | |
| DSC型距離和靈敏度校準(zhǔn)試塊 | |
| RC-分辨率對比試塊 | |
| (DS)類型-距離和靈敏度對比試塊 | |
| V3標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊 | |
| A型便攜式相控陣試塊 | |
| A型便攜式相控陣試塊 | |
| A型便攜式相控陣試塊翻轉(zhuǎn)架 | |
| B型便攜式相控陣試塊 | |
| B型便攜式相控陣試塊 | |
| B型便攜式相控陣試塊支架 | |
| API-1#試塊(1槽1孔) | |
| API-2#試塊(1槽1孔) | |
| API-3#試塊(1槽1孔) | |
| API-4#試塊(1槽1孔) | |
| API-5#試塊(1槽1孔) | |
| API-6#試塊(1槽1孔) | |
| API-1#試塊(2槽1孔) | |
| API-2#試塊(2槽1孔) | |
| API-3#試塊(2槽1孔) | |
| API-4#試塊(2槽1孔) | |
| API-5#試塊(2槽1孔) | |
| API-6#試塊(2槽1孔) | |
| API-7#試塊(2槽1孔) | |
| API-8#試塊(2槽1孔) | |
| API-9#試塊(2槽1孔) | |
| 日本標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊JIS-STB-A1 | |
| 日本標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊JIS-STB-A2 | |
| 日本標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊JIS-STB-A3 | |
| 日本標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊JIS-STB-G | |
| 日本標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊STB-A21 | |
| 日本標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊STB-A22 | |
| 日本標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊RB-A4AL | |
| 日本標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊RB-D | |
| 日本標(biāo)準(zhǔn)試塊RB-4 |

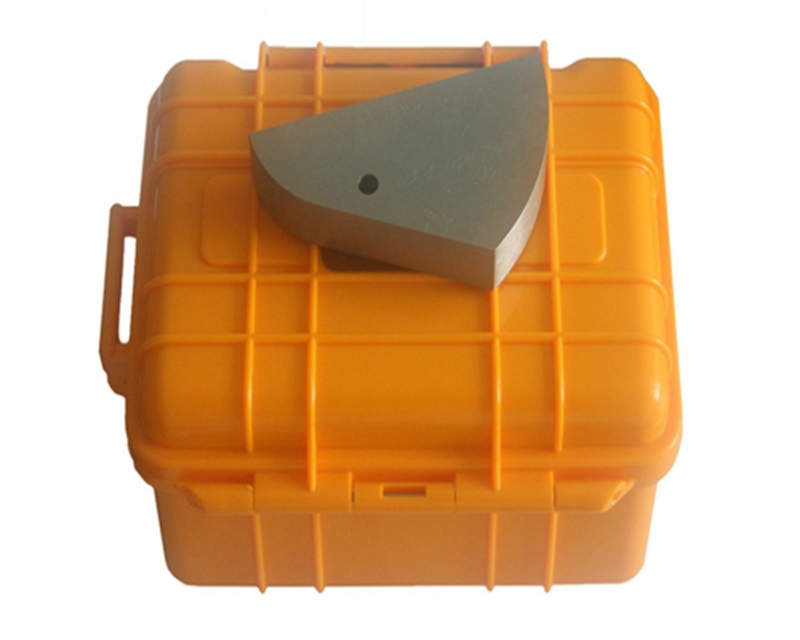
內(nèi)包裝橙色工程塑料

外包裝(紙箱)













